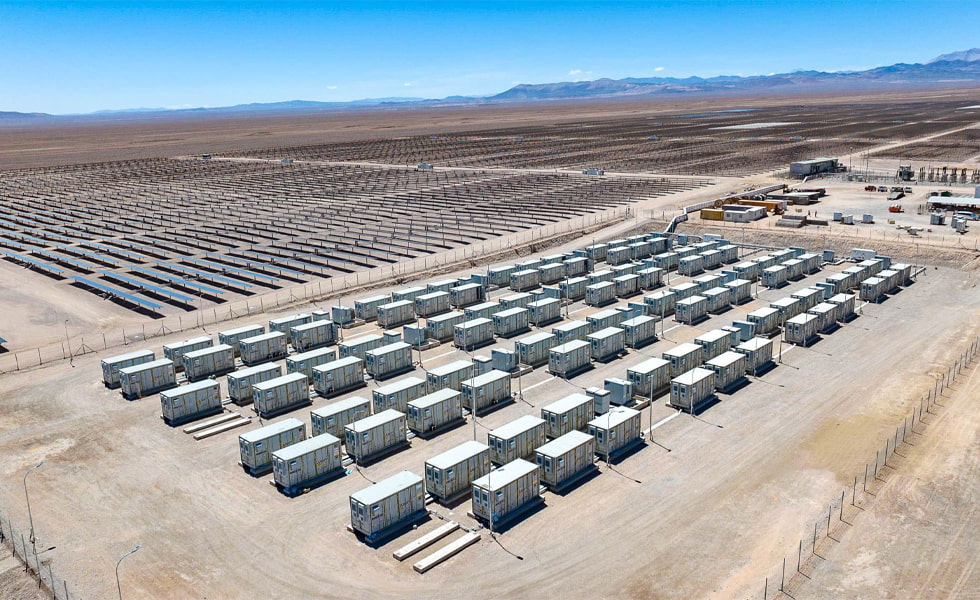
When discussing energy storage projects, the terms MW and MWh appear frequently. Many people are confused by these two abbreviations: what exactly do they mean and what's the difference? Simply put, MW is a unit of power, and MWh is a unit of energy. In power systems, MW and MWh are core metrics for describing system capabilities. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is as crucial as understanding the difference between speed and range.
I. Definition: The Essential Difference Between Power and Energy MW (Megawatt)—The "Speed" Measure of Energy
• MW is a unit of power, indicating the rate of energy conversion. 1MW = 1000kW (Kilowatts). The power level determines how much energy storage system can release or absorb per unit time, directly affecting its peak and frequency regulation capabilities. For example, a 100MW/200MWh energy storage plant can theoretically store or release 100MWh of energy (or 100,000 kWh) per hour.
Analogy: MW is like a car's "top speed," determining how fast it can go. • MWh (Megawatt-hour) – Energy "Capacity" Metric
MWh is a unit of energy, representing the product of power and time. 1MWh = 1000kWh (Kilowatt-hour), commonly known as "1000 kilowatt-hours of electricity." Capacity determines how much energy storage system can store or release, directly impacting its economic viability and application scenarios. For example, a 100MW/200MWh energy storage plant, if discharging at 100MW, can theoretically provide continuous power for two hours.
Analogy: MWh is like the "gas tank capacity" of a car, determining its range.
2. Why Energy Storage Projects Use Both Numbers:
In energy storage systems, MW and MWh are often mentioned together, such as "100MW/200MWh lithium iron phosphate battery energy storage system." Their combination describes the system's overall performance: 100MW represents the maximum power it can simultaneously deliver to or absorb from the grid, determining its peak and frequency regulation capabilities. 200MWh represents total energy capacity, which determines how long peak shaving and valley filling can be sustained. If discharged at a maximum power of 100MW, all the energy can be released within two hours; if discharged at 50MW, it can last for four hours. MW and MWh, like a speedometer and a mileagemeter, together define the core capabilities of energy storage systems.