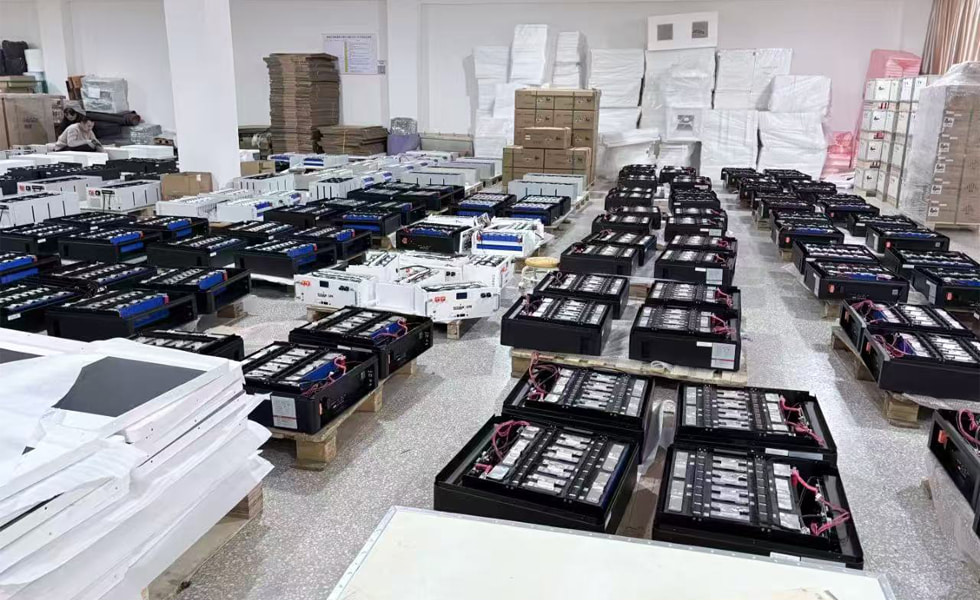
Lithium-ion Battery Energy Storage Working Principle
According to incomplete statistics from the CNESA DataLink global energy storage database, as of the end of December 2025, my country's cumulative installed capacity of power energy storage reached 213.3 GW, an increase of 54% year-on-year.
It is worth noting that new energy storage represented by lithium batteries has become the fastest-growing energy storage business. According to Chen Haisheng, as of the end of December 2025, my country's cumulative installed capacity of new energy storage reached 144.7 GW, an increase of 85% year-on-year. Based on current installed capacity data, by the end of 2025, most provinces in China had already achieved the targets set during the 14th Five-Year Plan period.
Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most mature and rapidly developing electrochemical energy storage technology, and will remain the leading technology for new energy storage development in the short term.
They consist of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, and an electrolyte. Currently, mainstream products commonly use nickel-manganese-cobalt ternary materials or lithium iron phosphate for the positive electrode, while the negative electrode is mostly made of carbon materials such as graphite.
Lithium-ion battery energy storage systems boast advantages such as high energy density, no memory effect, rapid charging and discharging, fast response, flexible configuration, and short construction cycles, making them widely applicable in energy storage projects on the generation side, grid side, and user side of new energy sources like wind and solar power.
The working principle of a lithium-ion battery energy storage system is to utilize the migration of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes to achieve the process of charge and discharge, thereby storing and releasing electrical energy.
Specifically, a lithium-ion battery energy storage system consists of multiple lithium-ion battery cells, each including a positive electrode, a negative electrode, and an electrolyte. A membrane separates the positive and negative electrodes, but the electrolyte can pass through the membrane, forming ion channels.
When the lithium-ion battery energy storage system needs to store electrical energy, an external power source delivers electrical energy to the system through a charger. The electrical energy is converted into chemical energy and stored between the positive and negative electrodes of the lithium-ion battery cells through the ion channels. During this process, ions migrate from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, forming a chemical reaction.
When electrical energy is needed, the lithium-ion battery energy storage system converts the stored electrical energy into direct current (DC) output. This DC output is then processed by devices such as inverters and supplied to external loads. During this process, lithium ions migrate from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, releasing chemical energy and generating electrical output.
The performance of a lithium-ion battery energy storage system is affected by various factors, such as the number of individual battery cells, electrochemical performance, battery pack structure, and control and management systems. Different application scenarios require the design and selection of appropriate lithium-ion battery energy storage systems based on specific needs.